


Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-08 Origin: Site








Use the formula Amp Hours = Watt Hours ÷ Voltage to convert energy storage between units easily.
Watt hours measure total energy, while amp hours measure electric charge over time; both are needed to size batteries correctly.
Always check your battery’s voltage before calculating to avoid errors and ensure accurate results.
Consider battery efficiency, voltage changes, and system needs when planning your solar power setup.
Accurate conversion helps you choose the right battery size, prevent power shortages, and optimize your solar system’s performance.
You can think of watt hours as the total amount of energy your battery can deliver over time. Imagine a magic box that powers a light bulb. If you run a 100-watt bulb for one hour, you use 100 watt hours of energy. This measurement shows how much energy you consume, not just how fast you use it. In electrical engineering, watt hours represent the cumulative effect of power over time. For example, a 60-watt device running for three hours will consume 180 watt hours. You determine watt hours by multiplying the power in watts by the time in hours. This unit helps you understand how much energy your devices need and how long your battery can support them.
Amp hours measure the amount of electric charge your battery can supply over a period. Picture a river of energy flowing from your battery. If your battery has a rating of 10 amp hours, it can deliver 10 amps for one hour or 1 amp for 10 hours. Amp hours focus on the current your battery can provide, not the total energy. This measurement is crucial when you want to know how long your battery can run a device at a certain current. However, amp hours alone do not tell you the full story about energy storage, especially when comparing batteries with different voltages.
Understanding the relationship between watt hours and amp hours is essential for anyone working with solar power systems. The main difference lies in what each unit measures. Watt hours represent total energy, while amp hours measure electric charge. The relationship between the two depends on voltage. You use the formula: watt hours = amp hours × voltage. This relationship allows you to compare batteries with different voltages and capacities.
Tip: When designing a solar battery system, always consider both watt hours and amp hours. Watt hours give you a complete picture of energy storage, while amp hours show how much current your battery can supply.
Amp hours measure electric charge over time, without considering voltage.
Watt hours measure total energy, combining voltage and current over time.
You can only compare batteries accurately by looking at watt hours, especially if they have different voltages.
Knowing both values helps you size your solar system, predict runtime, and optimize energy use.
In solar applications, watt hours reflect the total usable energy, while amp hours indicate how long your battery can deliver current. Both play a vital role in battery performance and system efficiency. By understanding the relationship between watt hours and amp hours, you can make informed decisions about battery selection and system design.
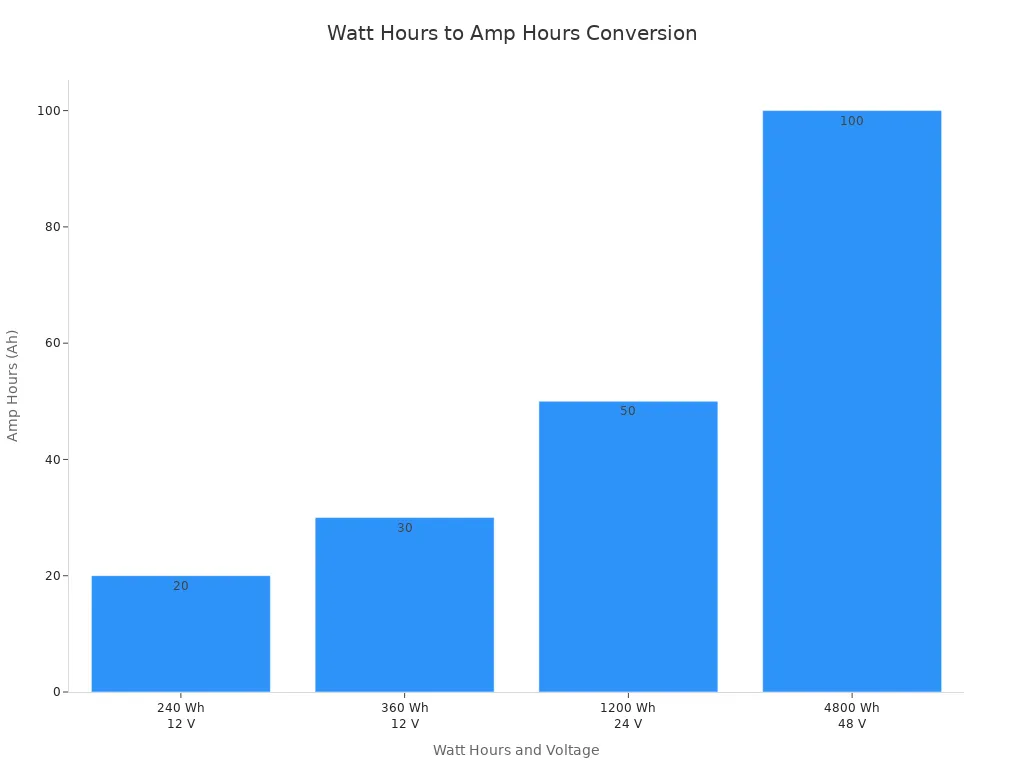
When you want to convert watt hours to amp hours, you use a simple formula:
Amp Hours (Ah) = Watt Hours (Wh) ÷ Voltage (V)
This formula helps you calculate how much electric charge your battery can deliver based on its energy storage and voltage. For example, if you have a battery with 4800 watt hours and a voltage of 48 volts, you divide 4800 by 48. The result is 100 amp hours. This calculation gives you a clear understanding of your battery’s capacity.
You can use this formula for any battery or solar power system. The process stays the same whether you work with 12V, 24V, or 48V systems. Here is a quick reference table to help you visualize the conversion:
Watt Hours (Wh) | Voltage (V) | Amp Hours (Ah) |
|---|---|---|
240 | 12 | 20 |
360 | 12 | 30 |
1200 | 24 | 50 |
4800 | 48 | 100 |
If you need to convert amp hours to watt hours, just reverse the formula: multiply amp hours by voltage. This approach works for both small and large solar setups.
Voltage plays a critical role in every watt hours to amp hours conversion. You must use the correct voltage to get accurate results. Most solar power systems use standard voltages like 12V, 24V, or 48V. Small systems, such as those in RVs or cabins, often use 12V batteries. Larger systems use 24V or 48V to reduce current and minimize energy loss.
⚡ Tip: Always check your battery’s voltage before you calculate amp hours. Using the wrong voltage can lead to incorrect results and poor system performance.
Voltage in batteries can change during use. For example, a lithium-ion battery might start at 29V when fully charged and drop to 20V when discharged. If you use a fixed voltage for your calculation, you get only an estimate. Real-world results may vary because the current increases as voltage drops to maintain the same power output. This is why watt hours provide a more stable measure of energy capacity than amp hours.
When you convert watt hours to amp hours, always use the nominal voltage of your system. This practice ensures your calculations match the actual performance of your solar power setup. By understanding the relationship between watt hours, amp hours, and voltage, you can size your batteries correctly and keep your energy system running smoothly.
You can easily calculate watt hours to amp hours by following a straightforward process. This method works for any battery system, whether you use it for solar, RV, or backup power applications. Here’s how you do it:
Identify your battery’s voltage. Most solar power systems use 12V, 24V, or 48V batteries. You can find this information on the battery label or in the manual.
Determine the watt hours you want to convert. This value might come from your battery’s specifications or your energy usage calculations.
Use the formula:Amp Hours (Ah) = Watt Hours (Wh) ÷ Voltage (V)
Substitute your values into the formula. For example, if your battery stores 1800 watt hours and operates at 12 volts, calculate 1800 ÷ 12 = 150 amp hours.
If you do not know your battery’s voltage or watt hours, check the manufacturer’s documentation or use a watt hours to amp hours calculator for quick results.
Rearrange the formula if you need to solve for a different variable. For example, to calculate watt hours, multiply amp hours by voltage.
Tip: Always double-check your voltage and watt hour values before starting your calculation. This step ensures you get accurate results every time.
Let’s look at some practical examples to help you master calculating watt hours to amp hours for different battery systems:
Suppose you have a 12V battery and want to know how many amp hours it provides if it stores 1200 watt hours.
Formula: Ah = Wh ÷ V
Calculation: 1200 Wh ÷ 12 V = 100 Ah
Your 12V battery with 1200 watt hours delivers 100 amp hours.
Now, imagine you use a 24V battery with 240 watt hours.
Formula: Ah = Wh ÷ V
Calculation: 240 Wh ÷ 24 V = 10 Ah
A 24V battery with 240 watt hours provides 10 amp hours.
If you have a 48V battery storing 4800 watt hours:
Formula: Ah = Wh ÷ V
Calculation: 4800 Wh ÷ 48 V = 100 Ah
This 48V battery offers 100 amp hours.
Battery Voltage (V) | Watt Hours (Wh) | Amp Hours (Ah) |
|---|---|---|
12 | 1200 | 100 |
24 | 240 | 10 |
48 | 4800 | 100 |
Note: You can use a watt hours to amp hours calculator for quick conversions, especially when working with multiple batteries or complex systems.
When calculating watt hours to amp hours, you need to avoid several common errors that can lead to inaccurate results or even damage your battery system:
Using the wrong voltage: Always confirm your battery’s voltage before performing any conversion. Even small differences can affect your results.
Ignoring nominal voltage variations: Battery voltage can fluctuate during use. For example, a 12V battery may actually operate slightly above or below 12 volts. Use the nominal voltage for calculations, but remember that real-world performance may vary.
Overlooking environmental factors: Temperature and discharge rates can impact battery capacity. High loads or extreme temperatures may reduce the actual amp hours available.
Mixing batteries with different voltages: Connecting batteries with different voltages can cause uneven charging and discharging. This practice can shorten battery life and create safety hazards.
Not considering battery efficiency: Real batteries are not 100% efficient. Losses due to heat, age, or internal resistance can reduce the usable amp hours.
⚠️ Alert: For the most accurate results, always use batteries with the same voltage, chemistry, and age in your system. This approach ensures your watt hour to amp hour calculations reflect real-world performance.
By following these steps and avoiding common mistakes, you can confidently calculate watt hours to amp hours for any battery system. This knowledge helps you size your solar power setup, select the right batteries, and keep your energy system running smoothly.

Understanding the conversion from watt hour to amp hour is crucial when you design or upgrade solar power systems. This conversion links your total energy consumption, measured in watt hours, with the capacity of a battery, which is typically rated in amp hours and depends on system voltage. When you know how to convert watt hours to amp hours, you can accurately size your battery bank to meet your daily energy needs. This process helps you avoid undersizing, which can lead to power shortages, and oversizing, which increases costs without adding value.
You use watt hours to plan your total energy consumption, while amp hours help you determine the right battery size and expected runtime. By mastering this relationship, you ensure your solar power system delivers reliable performance and meets your energy storage capacity requirements. Proper conversion also allows you to factor in battery type, discharge rates, and system voltage, optimizing both performance and battery lifespan. For example, if you need to run essential appliances overnight, calculating the correct amp hours ensures your battery bank can handle the load without risking deep discharge or premature failure.
To achieve the best results when sizing batteries for solar energy storage, follow these best practices:
Check Device Wattage and Battery Specs
Review the voltage and capacity markings on your battery label.
Consult the manufacturer’s documentation or website for detailed specifications.
Refer to the user manual or datasheet for watt hour or amp hour ratings.
Use battery analyzers for precise measurements if available.
Contact the manufacturer or a professional if you have doubts.
Use the Correct Formula
Apply the formula:
Amp Hours (Ah) = Watt Hours (Wh) ÷ Voltage (V)
Always use the actual voltage of your system for accurate results.
Consider Battery Efficiency
Remember that the capacity of a battery is affected by efficiency factors such as depth of discharge, battery chemistry, and battery management systems.
Not all of the rated amp hours are usable in real-world solar applications. For example, lithium batteries with advanced management systems often provide higher usable capacity compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Plan for Growth and Autonomy
Anticipate future increases in energy demand. If you plan to add more appliances, ensure your battery bank can handle the extra load.
Factor in days of autonomy, especially for off-grid solar power systems, to maintain power during cloudy weather or unexpected outages.
�� Tip: Accurate amp hour calculations prevent both power shortages and unnecessary expenses. Use digital calculators to minimize manual errors and ensure your battery sizing matches your solar power system’s needs.
By following these steps, you can confidently select the right battery capacity, optimize your energy storage capacity, and ensure your solar power systems operate efficiently and reliably.
To convert watt hours to amp hours, follow these steps:
Find your battery’s amp hour rating.
Check the battery voltage.
Use the formula: Watt Hours = Amp Hours × Voltage.
Double-check your calculations for accuracy.
Accurate conversion helps you size your battery bank and ensures your solar power system meets your energy needs. This relationship between watt hours and amp hours lets you plan for reliable energy storage and avoid common mistakes. Apply these steps to your own battery setup for better energy planning.
You can check the battery label or user manual. Manufacturers usually print the voltage rating clearly. If you cannot find it, use a multimeter to measure the voltage directly.
Yes, you can use the formula for lithium, lead-acid, or AGM batteries. Always use the correct voltage for your specific battery type to ensure accurate results.
Amp hours show how long your battery can supply current. Watt hours reveal the total energy available. You need both values to size your battery bank and match your energy needs.
Using the wrong voltage gives you inaccurate amp hour results. This mistake can lead to undersized or oversized battery banks, which affects system performance and reliability.
You can use online calculators or conversion tables. Enter your watt hours and voltage, and the tool provides the amp hours instantly. This method saves time and reduces calculation errors.
The Future of Ground-Mounted Solar Systems: Sustainability and Scalability in Renewable Energy
Innovative Ground-Mounted Solar Racking Systems: Trends and Technologies to Watch
Top Trends in Ground-Mounted Solar Mounting Systems for 2024: Innovations to Watch
Solar Roof Mounting Systems: The Key Support for Green Energy
The Latest Innovations in Solar Mounting Systems: What to Expect in 2024