


Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-05 Origin: Site








When working with solar power systems, it’s important to understand how to convert watts to kilowatts to accurately size your installation.
To convert Watts (W) to Kilowatts (kW), you must divide the wattage value by 1,000. The formula is: $kW = W / 1,000$.
For instance, if your solar power systems use 300 watts, divide 300 by 1,000 to get 0.3 kilowatts.
If your goal is a 6 kilowatt solar power system, you would need twenty 300-watt panels.
Mastering the watts to kilowatts conversion helps you interpret solar panel specifications and select the ideal mounting solution, such as Haina Solar’s reliable roof mounts, for your solar power systems.
Divide watts by 1,000 to convert them into kilowatts easily and accurately.
Understanding watts and kilowatts helps you size your solar power system correctly.
Power (watts) shows how fast energy is used; energy (kilowatt-hours) shows total electricity used over time.
Check solar panel labels for wattage to calculate total system kilowatts and plan your installation.
Avoid common mistakes like forgetting to divide by 1,000 or misplacing decimal points.
Use online calculators to save time and reduce errors when converting watts to kilowatts.
Accurate conversions help you choose the right solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems.
Double-check your math and units to ensure your solar system meets your energy needs safely.

You often see the terms watt and kilowatt when working with solar power systems. A watt is the basic unit of power in the metric system. It measures the rate at which energy is used or produced at any moment. The watt is named after James Watt, a Scottish inventor who made significant contributions to the development of the steam engine.
A kilowatt is simply 1,000 watts. The prefix "kilo-" means you multiply the base unit by 1,000. This relationship is similar to how a kilometer equals 1,000 meters. If you want to know how many watts are in a kilowatt, the answer is always 1,000. For example, a solar array that produces 8,000 watts has a capacity of 8 kilowatts. You can convert watts to kilowatts by dividing the number of watts by 1,000. If you have a 2,500-watt heater, it uses 2.5 kilowatts.
Tip: Remember, the formula is simple—divide the number of watts by 1,000 to get kilowatts.
Here is a quick reference table to help you visualize the relationship:
| Power (Watts) | Power (Kilowatts) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 0.1 |
| 500 | 0.5 |
| 1,000 | 1 |
| 2,500 | 2.5 |
| 5,000 | 5 |
You need to understand the difference between power and energy when planning a solar installation. Power, measured in watts or kilowatts, shows the rate at which your system uses or generates electricity at any given moment. Think of power as the speedometer in your car—it tells you how fast you are going right now.
Energy, on the other hand, is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). It represents the total amount of electricity used over a period of time. This is like the odometer in your car, which shows the total distance you have traveled. For example, if you run a 100-watt device for 10 hours, you use 1 kilowatt-hour of energy.
Understanding this distinction is important. Power ratings in kilowatts help you size your solar system and make sure it can handle your needs. Energy consumption in kilowatt-hours determines your electricity bill and helps you manage costs.
Power (watts or kilowatts): Instantaneous rate of energy use or production.
Energy (kilowatt-hours): Total amount of electricity used over time.
By knowing the difference, you can select the right equipment, plan your installation, and track your energy usage more effectively.
To convert watts to kilowatts, you need to use a simple mathematical formula. The SI prefix "kilo-" means 1,000 times the base unit. This means that one kilowatt equals 1,000 watts. You can use the following formula:
kilowatts (kW) = watts (W) ÷ 1,000
This formula comes directly from the definition of a kilowatt. Power is measured in watts, which is one joule per second. When you want to express a larger amount of power, you use kilowatts. For example, if you have a device rated at 2,000 watts, you divide by 1,000 to get 2 kilowatts.
Tip: Always remember that dividing by 1,000 is the key step when you convert watts to kilowatts.
You can follow a clear process to convert watts to kilowatts. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Identify the wattage of your device or system. For example, you might have a solar panel rated at 1,400 watts.
Divide the wattage by 1,000. This step changes the unit from watts to kilowatts.
Write down the result as kilowatts. For example, 1,400 watts ÷ 1,000 = 1.4 kilowatts.
Let’s look at another example:
Suppose you have a solar inverter rated at 2,500 watts.
Divide 2,500 by 1,000.
The result is 2.5 kilowatts.
You can use this method for any wattage value. This process helps you compare different solar components and plan your system size accurately.
Example Table:
Device Power (Watts) Power (Kilowatts) Solar Panel 300 0.3 Inverter 2,500 2.5 Heater 1,000 1
When you convert watts to kilowatts, you might make some common errors. Being aware of these mistakes helps you avoid problems in your calculations.
Forgetting to divide by 1,000: Some people skip the division step and write the watt value as kilowatts. This leads to incorrect system sizing.
Misplacing the decimal point: If you divide incorrectly, you might end up with a number that is too large or too small. For example, writing 2,500 watts as 25 kilowatts instead of 2.5 kilowatts.
Mixing up units: Always check if your value is in watts or kilowatts before making decisions about your solar system.
Using the wrong formula: Sometimes, people multiply instead of divide. Remember, to convert watts to kilowatts, you always divide by 1,000.
Note: Double-check your calculations and units every time you work with power ratings. This ensures your solar installation meets your needs and matches the specifications of products like Haina Solar’s mounting systems.

When you plan a solar installation, understanding the conversion from watts to kilowatts is essential. This conversion helps you determine the right size for your solar power systems. If you miscalculate, you might end up with a system that cannot meet your energy needs or one that costs more than necessary. Accurate conversion from watts to kilowatts allows you to estimate the power capacity and energy storage requirements for your home or business.
For example, if your household uses 4,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per year, you need to know how many kilowatts your solar panels must produce to cover this demand. Most residential solar panels have wattage ratings between 350 and 425 watts. To find out how many kilowatts your system should provide, you divide the total wattage of all panels by 1,000. If you install 15 panels rated at 400 watts each, your system will have a total capacity of 6,000 watts, or 6 kilowatts.
Accurate conversion from watts to kilowatts ensures your solar power systems are neither undersized nor oversized. This precision supports better energy planning, cost savings, and system reliability.
When designing solar systems, you must also consider factors like solar module efficiency, weather conditions, and your location. These factors, combined with correct conversion, help you select the right number of panels and the best mounting solution. Haina Solar’s Solar Panel Roof Mounts provide a reliable foundation for your installation, supporting a wide range of panel sizes and system capacities. Knowing exactly how many kilowatts your system will produce helps you choose the right mounting system and ensures a smooth installation process.
Reading and understanding solar panel specifications is a key step in building efficient solar power systems. Every solar panel comes with a label that shows its wattage rating, usually between 250 and 400 watts for most residential solar panels. This number tells you the maximum power output under standard test conditions. To figure out how many kilowatts your entire system will produce, you add up the wattage of all your panels and convert the total from watts to kilowatts.
For example, if you want to know how many kilowatts do solar panels produce in your setup, you need to look at the panel specs and do the math. If you have 20 panels rated at 350 watts each, your system will generate 7,000 watts, or 7 kilowatts. This total system capacity influences your installation design, the number of panels you need, and the type of inverter required.
Tip: Always check the panel’s efficiency rating. Higher efficiency panels convert more sunlight into electricity, which means you can generate more power with fewer panels and less roof space.
Accurate conversion from watts to kilowatts also plays a major role in cost estimation. Most installers use the price-per-watt metric to calculate the total cost of your solar power systems. For example, if your 10-kilowatt system costs $30,000, the price per watt is $3.00. If you make a mistake in converting watts to kilowatts, your cost estimates will be off, which can affect your budget and your return on investment.
Haina Solar’s Solar Panel Roof Mounts are designed to handle a wide range of system sizes. Whether you are installing a small residential system or a large commercial array, knowing how many kilowatts your system will produce helps you select the right mounting solution. This ensures your installation is safe, efficient, and cost-effective.
You often see kilowatt-hours (kWh) on your electricity bill or in solar energy discussions. A kilowatt-hour measures energy, not power. It tells you how much electricity you use or produce over time. One kilowatt-hour equals using 1,000 watts for one hour. For example, if you run a 1,000-watt heater for one hour, you use 1 kWh. If you use a 100-watt light bulb for 10 hours, you also use 1 kWh. This unit combines power (watts) and time (hours) to show total energy.
You calculate kilowatt-hours by multiplying the power in watts by the number of hours, then dividing by 1,000. The formula looks like this:
kWh = (watts × hours) / 1,000
This formula helps you understand how much energy your devices or solar panels generate or consume. For example, if you have a 1,500-watt appliance running for 2.5 hours, you get:
kWh = (1,500 × 2.5) / 1,000 = 3.75 kWh
Understanding kWh helps you compare energy use, estimate costs, and plan your solar system size. It also helps you when you need to convert kwh to watts for system sizing or energy tracking.
Kilowatt-peak (kWp) is a term you see on solar panel labels. It shows the maximum power a solar panel or system can produce under ideal conditions. Manufacturers test panels in the lab using Standard Test Conditions (STC):
Solar irradiance of 1,000 watts per square meter
Cell temperature of 25°C
Air mass of 1.5
A solar panel rated at 0.3 kWp can produce 0.3 kilowatts at peak sunlight. This rating helps you compare different panels and systems. For example, a 100 kWp solar farm can deliver 100 kilowatts at peak sunlight, but real-world output changes with weather, temperature, and location.
Manufacturers use kWp to classify panels and help you size your solar installation. The kWp value is like a car’s horsepower rating—it shows the maximum possible output, not the average daily production. When you plan your solar project, knowing the kWp helps you estimate how much energy you can expect under the best conditions. You may also need to convert kwh to watts when comparing system performance or planning upgrades.
You often need to convert between kWh and watts when working with solar power systems. The most common question is how to convert kwh to watts. The process involves understanding the relationship between power, time, and energy.
To convert kWh to watts, use this formula:
Watts = (kWh × 1,000) / hours
If you know the energy in kWh and the number of hours, you can find the average power in watts. For example, if your solar panels generate 2 kWh over 4 hours, the average power is:
Watts = (2 × 1,000) / 4 = 500 watts
You can also convert watts and hours to kWh using the earlier formula. For example, a 250-watt solar panel exposed to 4 hours of sunlight produces:
kWh = (250 × 4) / 1,000 = 1 kWh
This calculation helps you estimate daily or monthly energy production. You use these conversions to size your solar system, compare products, and track performance. When you review your solar panel output or your electricity bill, you may need to convert kwh to watts to understand your system’s efficiency or to plan for future expansion.
Tip: Always check the units when you work with solar data. Mixing up kWh and watts can lead to mistakes in system sizing or cost estimates. Use the formulas above to convert kwh to watts or watts to kWh as needed.
A table can help you visualize these conversions:
| Power (Watts) | Time (Hours) | Energy (kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| 250 | 4 | 1 |
| 500 | 2 | 1 |
| 1,000 | 1 | 1 |
You can find more educational resources on kwh to watts conversions from university courses and engineering activities. These resources explain the difference between power and energy, and they provide hands-on examples using real solar panel data. Understanding kwh to watts and how to convert kwh to watts gives you the confidence to manage your solar power system effectively.
You can save time and reduce errors by using online calculators when converting watts to kilowatts. Reliable tools like the ShopSolarKits.com watts to kWh calculator have earned the trust of thousands of users. This calculator uses the standard formula, kWh = (watts × hours) / 1,000, which ensures accurate results as long as you enter the correct values. The site also explains the difference between watts and kilowatt-hours, helping you understand your calculations. Another dependable option is CalculatorSoup.com, which offers a power conversion calculator that follows internationally accepted conversion factors. These calculators use precise mathematical relationships, such as 1 kW = 1,000 W, so you can trust the results for your solar project planning.
Tip: Always double-check your input values for the most accurate conversion results.
When you examine product labels on solar panels, inverters, or other electrical equipment, you will find important information about wattage and kilowatt ratings. Labels typically display voltage, current, and power ratings, either in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). You may also see the type of power supply, such as AC or DC, and sometimes frequency and fuse ratings. The power rating tells you how much energy the product uses or produces. For higher-powered devices, the label will show kilowatts. Understanding these numbers helps you match your equipment to the right power source and avoid overloading your system.
You should interpret this data by checking that the voltage and current ratings fit your installation. For example, if a solar panel label shows 400 W and 40 V, you know the panel produces 400 watts at its rated voltage. This information helps you calculate total system output and ensures you select compatible components. Knowing the power rating also lets you compare the efficiency of different products, so you can make informed decisions for your solar setup.
Note: Always read product manuals and labels carefully to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Careful installation planning ensures your solar power system operates efficiently and meets your energy needs. Haina Solar’s mounting systems play a key role in this process. Their solutions support accurate system sizing and smooth installation through several features:
Racking systems withstand snow loads up to 2,400 Pa and wind speeds up to 60 m/s, providing stability in harsh conditions.
Modular designs and compatibility with various panel sizes allow you to tailor your system to your specific site and energy requirements.
Technical support and training from Haina Solar’s team help you achieve optimal performance and avoid installation errors.
Customizable mounts adapt to residential, commercial, and industrial projects, ensuring flexibility and precise system sizing.
Innovative features, such as tracking systems and IoT-enabled monitoring, boost energy yield and simplify ongoing maintenance.
By choosing a reliable mounting solution, you streamline the installation process and maximize your solar investment. Haina Solar’s expertise and comprehensive support make it easier for you to plan, size, and install your solar power system with confidence.
Decimal placement errors often cause confusion when you convert watts to kilowatts. You might see unexpected results if you misplace the decimal or use the wrong conversion factor. Here are some of the most frequent mistakes and how you can avoid them:
Confusing power (watts) with energy (kilowatt-hours), which leads to incorrect unit assumptions.
Using the wrong conversion factor, such as dividing by 100 instead of 1,000, which can result in large miscalculations.
Ignoring the "kilo-" prefix, causing you to underestimate values by a factor of 1,000.
To prevent these errors, follow these strategies:
Always check the units before you start your calculation.
Use the correct conversion factor: 1 kilowatt equals 1,000 watts.
Pay close attention to prefixes and their magnitudes.
Double-check your math to confirm decimal placement and conversion accuracy.
Tip: Remember, you divide by 1,000 to convert watts to kilowatts. For example, 2,500 watts becomes 2.5 kilowatts.
If your calculated kilowatt value does not match what you expect, review your steps. Sometimes, the issue comes from treating apparent power (volt-amps, VA) as real power (watts) without considering the power factor. For accurate results, always verify the power factor and use the correct formula for your equipment.
| Issue Identified | Explanation | Impact | Recommended Troubleshooting Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assuming VA equals Watts | Treating apparent power (VA) as real power (Watts) | Undersized systems, inaccurate calculations | Use Watts = VA × Power Factor (PF); check specs for correct PF values (e.g., 0.8 for motors) |
| Ignoring Power Factor | Not accounting for PF in inductive loads | Inverter or battery overload | Size inverters/batteries based on VA, not just watts; use typical PF values (motors 0.7–0.8) |
| Overlooking Power Factor Change | Neglecting PF reduction in aging equipment | Reduced efficiency, possible system failures | Add a 10–20% buffer to VA ratings for older equipment; test PF before reuse |
Sometimes, you need to convert kilowatts back to watts. This reverse conversion is essential when you size generators, calculate electrical loads, or determine current (amps) from power and voltage. The process is simple: multiply the kilowatt value by 1,000.
For example, if you have a 5 kW system, you multiply 5 by 1,000 to get 5,000 watts. This step ensures you use the correct numbers for further calculations, such as finding the current in amps.
| Kilowatts (kW) | Conversion to Watts (W) | Voltage (V) | Calculated Amps (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 kW | 5 × 1,000 = 5,000 | 120 | 5,000 ÷ 120 = 41.67 |
| 10 kW | 10 × 1,000 = 10,000 | 240 | 10,000 ÷ 240 = 41.67 |
| 15 kW | 15 × 1,000 = 15,000 | 120 | 15,000 ÷ 120 = 125 |
| 20 kW | 20 × 1,000 = 20,000 | 240 | 20,000 ÷ 240 = 83.33 |
| 25 kW | 25 × 1,000 = 25,000 | 120 | 25,000 ÷ 120 = 208.33 |
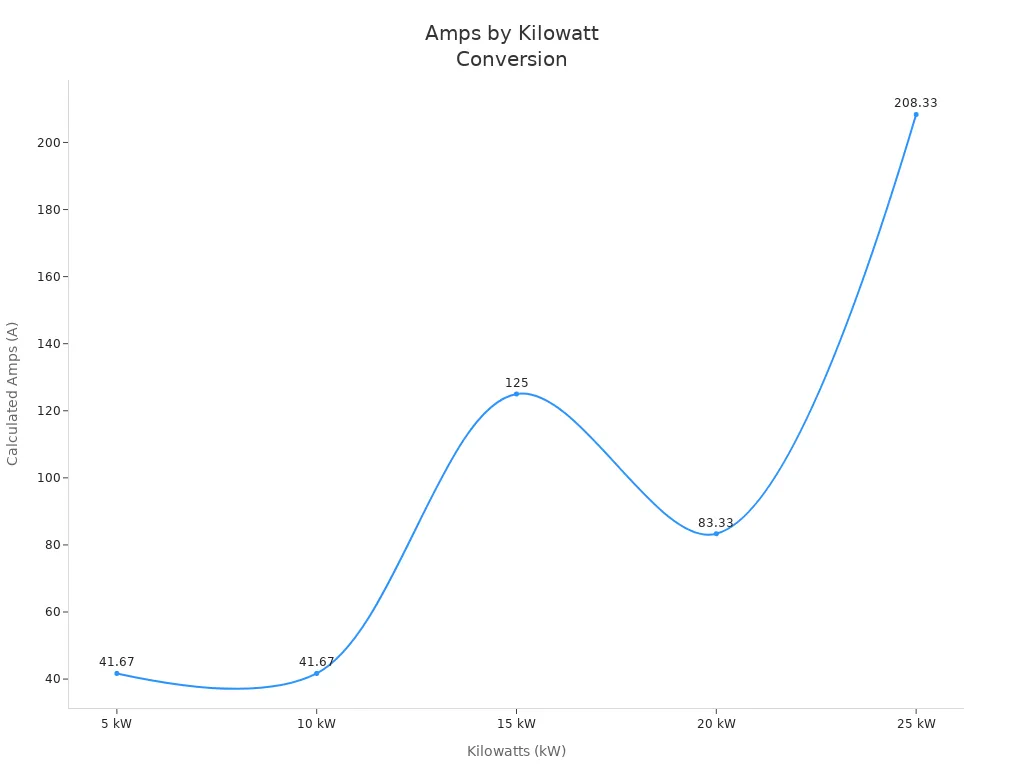
You often use this reverse conversion when you need to calculate the current for a specific voltage or when you want to check if your generator can handle the load. Always multiply kilowatts by 1,000 to get watts before you proceed with other calculations. This habit helps you avoid errors and ensures your solar power system operates safely and efficiently.
Note: Understanding these conversions and double-checking your calculations will help you avoid mismatched numbers and confusion with units. This attention to detail supports accurate system sizing and reliable solar installations.
Converting watts to kilowatts is simple but essential for solar power success.
Recognize that 1 kilowatt equals 1,000 watts.
Use the formula: kilowatts = watts ÷ 1,000.
Apply this in your solar project planning for accurate system sizing and energy management.
Accurate conversions help you avoid costly mistakes and optimize your installation.
Haina Solar’s mounting solutions support efficient, reliable solar setups.
For more guidance, explore industry resources or consult with solar professionals.
Master these steps to ensure your solar power system meets your needs and delivers lasting value.
Watts measure power at a specific moment. Kilowatts represent 1,000 watts. You use watts for small devices and kilowatts for larger systems. This distinction helps you compare and size solar equipment accurately.
You divide the number of watts by 1,000. For example, 2,000 watts divided by 1,000 equals 2 kilowatts. This formula works for any wattage value.
You need to convert watts to kilowatts to size your solar system correctly. Installers and manufacturers use kilowatts to describe system capacity. Accurate conversion ensures your system meets your energy needs.
Yes, you can use trusted online calculators for quick and accurate conversions. These tools help you avoid manual errors and save time during system planning.
Look for the “W” or “Watts” value on the label. This number shows the panel’s maximum power output. You can add up all panel wattages and convert the total to kilowatts for your system size.
Haina Solar’s mounts support various roof types and panel sizes. You can use them for residential, commercial, or industrial solar projects. Their design ensures easy installation and long-term durability.
Double-check your math and units. Make sure you divide by 1,000 when converting watts to kilowatts. If you still see errors, review the product label or consult a solar professional for guidance.